The fault divides into three segments each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk.
Does the san andreas fault make new ocean floor.
The san andreas fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly 1 200 kilometers 750 mi through california.
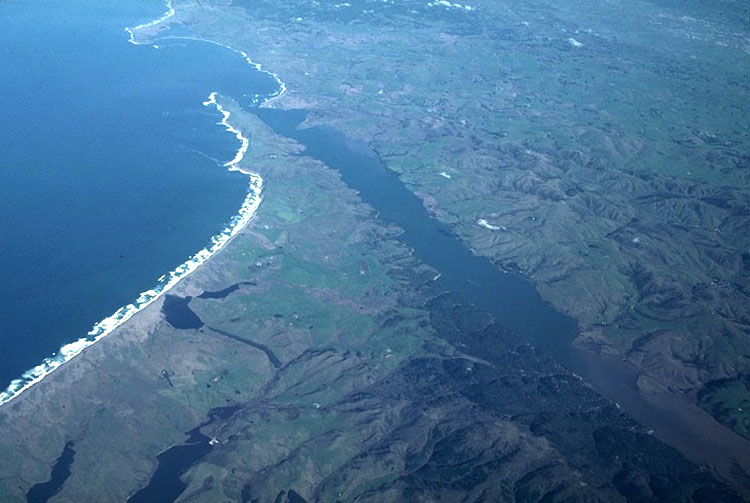
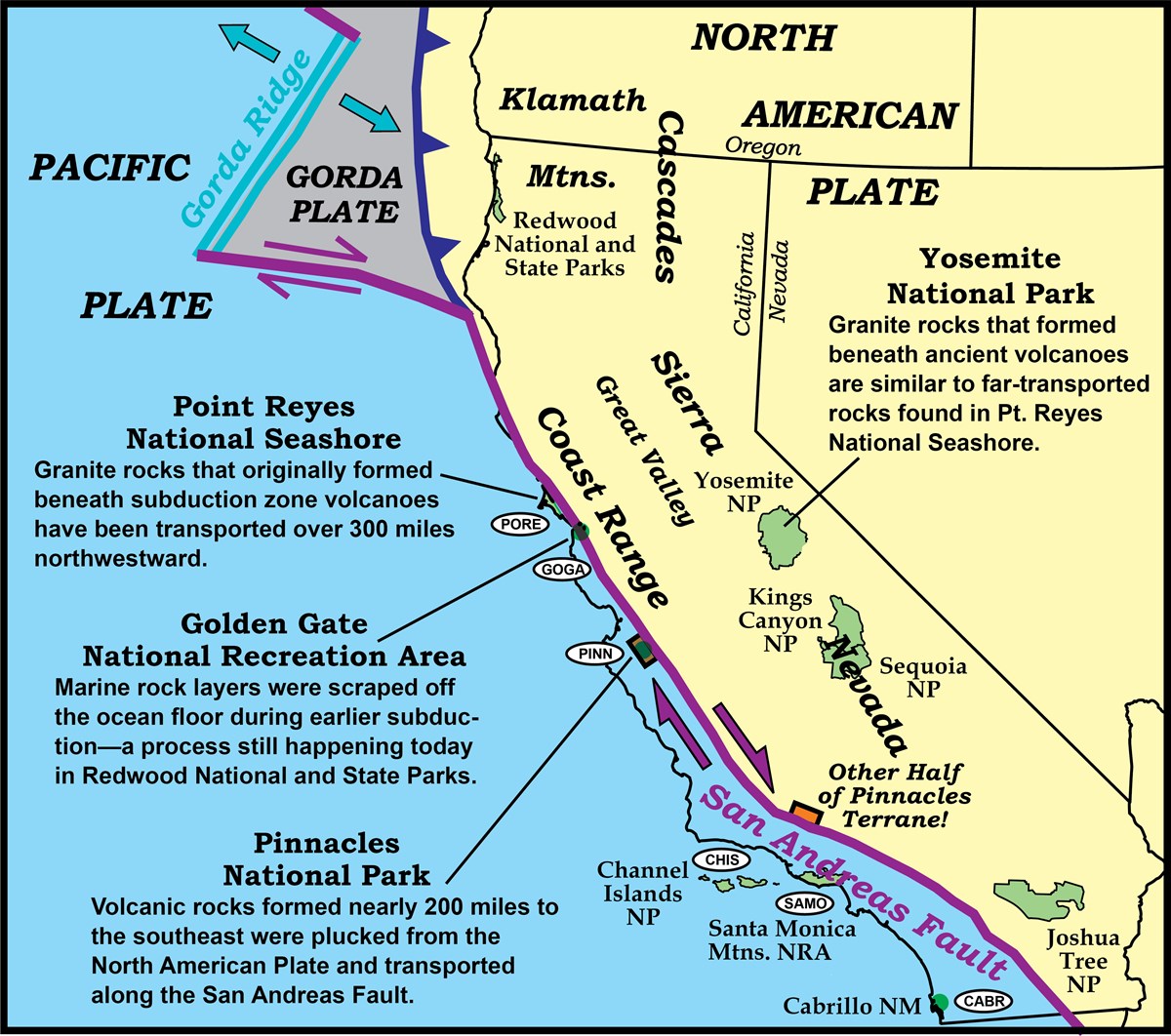
The north coast section of the san andreas fault is north of san francisco.
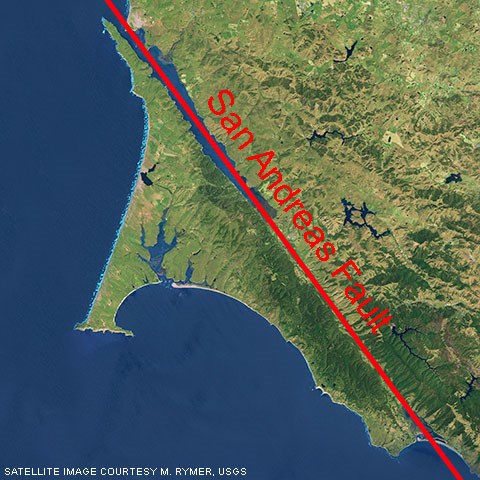
It runs most of the length of california and into the ocean.
For example in bodega bay the san andreas fault is actually located about 800 meters away from where it was thought to be.
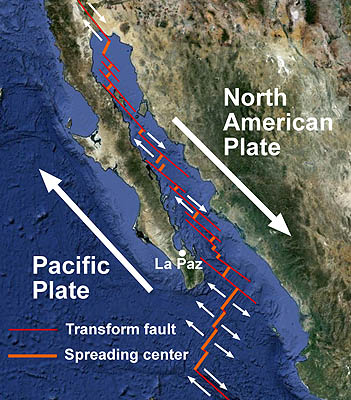
The san andreas fault connects two divergent fault boundaries in the north and south.
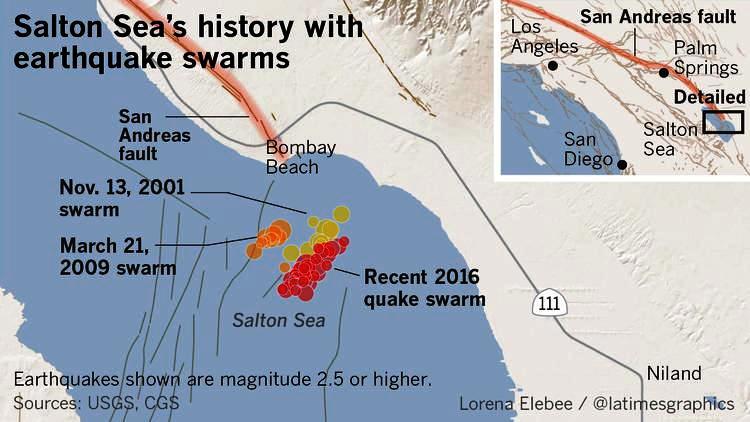
Prior to 1300 the intervals are shorter about 200 years.
It forms the tectonic boundary between the pacific plate and the north american plate and its motion is right lateral strike slip horizontal.
As the plates continue to move apart more and more new basaltic crust is created.
San andreas fault line map.
The scale of the project started in 2007 by the california ocean.
Most transform faults are underwater but the san andreas fault is one of the few that is exposed on land.
Transform faults have shallow earthquakes that are often quite damaging on land.
When the magma reaches water at the ocean floor most spreading centers are in the ocean it cools and hardens and becomes new oceanic crust.